What are the Maintenance Requirements for Four-Point Contact Ball Bearings?
Four-point contact ball bearings are specialized mechanical components designed to handle complex loads in various industrial applications. These bearings are engineered to support axial loads from both directions, radial loads, and moment loads simultaneously, making them a versatile choice for many machinery types. Proper maintenance of these bearings is crucial to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability in demanding operational environments.
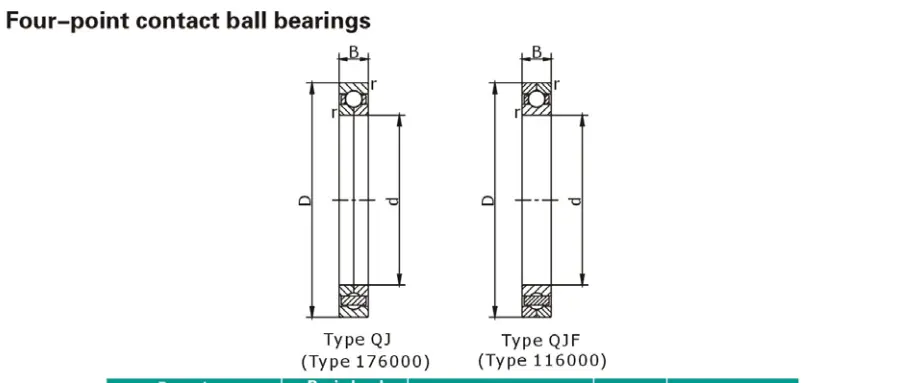
How do four-point contact ball bearings differ from other bearing types?
Four-point contact ball bearings stand out from other bearing types due to their unique design and load-bearing capabilities. Unlike conventional ball bearings that typically have two points of contact between the ball and the raceways, four-point contact bearings feature a specially designed raceway geometry that allows the balls to contact the inner and outer rings at four distinct points. This configuration offers several advantages:
1. Enhanced load capacity: The four-point contact design distributes loads more evenly across the bearing, allowing it to handle higher axial and moment loads compared to traditional ball bearings. This makes them particularly suitable for applications where space is limited, but load-bearing capacity is critical.
2. Increased stiffness: The unique contact pattern of these bearings results in greater overall stiffness, which is essential for maintaining precision in high-accuracy applications such as machine tool spindles, rotary tables, and robotic arms.
3. Reduced sensitivity to misalignment: The four-point contact geometry provides a degree of self-aligning capability, making these bearings more forgiving of slight misalignments that may occur during installation or operation.
4. Compact design: Four-point contact bearings can often replace multiple bearings in certain applications, leading to more compact and simplified machine designs. This can result in cost savings and improved overall system performance.
5. Bidirectional axial load support: Unlike angular contact bearings that are optimized for axial loads in one direction, four-point contact bearings can efficiently handle axial loads in both directions. This versatility eliminates the need for paired bearings in many applications.
6. Moment load capacity: The unique geometry of these bearings allows them to resist tilting moments effectively, making them ideal for applications where the shaft may experience bending or tilting forces.
Understanding these differences is crucial for maintenance personnel and engineers, as the unique characteristics of four-point contact bearings influence their maintenance requirements and operational considerations. For instance, the higher load capacity may allow for longer intervals between maintenance checks in some applications, while the increased stiffness might require more precise alignment during installation and more frequent monitoring of operating conditions to prevent premature wear.
What are the common applications of four-point contact ball bearings?

Four-point contact ball bearings find widespread use across various industries due to their versatile load-handling capabilities and compact design. Understanding the common applications of these bearings is essential for maintenance professionals, as it provides context for the specific challenges and requirements associated with different operational environments. Here are some of the most prevalent applications:
1. Machine tool industry: In machine tools, four-point contact bearings are often used in spindle assemblies, rotary tables, and indexing mechanisms. Their high stiffness and precision make them ideal for maintaining tight tolerances in cutting and grinding operations. For example, in CNC milling machines, these bearings help ensure the spindle's stability during high-speed rotations and under varying cutting loads.
2. Robotics and automation: The compact nature and multi-directional load-bearing capacity of four-point contact bearings make them excellent choices for robotic arm joints and wrist assemblies. They allow for smooth, precise movements while handling complex loads in various orientations. In pick-and-place robots used in manufacturing and packaging industries, these bearings contribute to increased accuracy and repeatability of movements.
3. Aerospace industry: Four-point contact bearings are used in aircraft landing gear mechanisms, flap actuators, and helicopter rotor systems. Their ability to handle combined loads and operate reliably under extreme conditions makes them suitable for these critical applications. For instance, in helicopter main rotor assemblies, these bearings help manage the complex forces acting on the rotor blades while ensuring smooth rotation.
4. Wind turbines: In wind energy systems, four-point contact bearings are often employed in pitch and yaw mechanisms. Their ability to handle both axial and radial loads while resisting moment loads is crucial for the precise control of blade pitch and nacelle orientation. This application requires bearings that can operate reliably in challenging outdoor environments and withstand varying wind loads.
5. Medical equipment: Precision medical devices such as CT scanners and MRI machines utilize four-point contact bearings in their rotating gantries. The high stiffness and accuracy of these bearings contribute to the clear, detailed images produced by these diagnostic tools. Maintenance in this sector is particularly critical, as equipment downtime can have significant impacts on patient care.
6. Heavy industry: In steel mills, mining equipment, and construction machinery, four-point contact bearings are used in various rotating assemblies subjected to heavy loads and harsh environments. For example, they may be found in the slewing rings of excavators or in the roller presses used in mineral processing.
7. Textile machinery: The textile industry employs these bearings in spinning frames, weaving looms, and knitting machines. Their ability to operate at high speeds while maintaining precision is vital for producing high-quality textiles efficiently.
8. Packaging equipment: In the packaging industry, four-point contact bearings are used in filling machines, capping machines, and other rotary systems where precise indexing and position control are essential for maintaining production quality and speed.
9. Renewable energy: Beyond wind turbines, these bearings find applications in solar tracking systems for large-scale solar farms. They help in accurately positioning solar panels to maximize energy capture throughout the day.
10. Marine applications: Ships and offshore platforms use four-point contact bearings in various systems, including propeller shafts, steering gear, and crane pedestals. Their resistance to corrosion and ability to handle shock loads make them suitable for marine environments.
Understanding these applications is crucial for maintenance teams as each environment presents unique challenges. For instance, bearings in outdoor wind turbines require different maintenance approaches compared to those in clean room medical equipment. Factors such as exposure to contaminants, temperature fluctuations, and load variations must be considered when developing maintenance strategies for four-point contact bearings in these diverse applications.
How can you extend the lifespan of four-point contact ball bearings?
Extending the lifespan of four-point contact ball bearings is crucial for maintaining equipment reliability and reducing overall maintenance costs. By implementing proper care and maintenance practices, you can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of these critical components. Here are key strategies to extend the lifespan of four-point contact ball bearings:
1. Proper lubrication:
- Use the correct type and amount of lubricant as specified by the bearing manufacturer.
- Establish a regular lubrication schedule based on operating conditions and manufacturer recommendations.
- Monitor lubricant condition and replenish or replace as needed to prevent dry running or contamination.
- Consider automated lubrication systems for consistent and precise lubrication in critical applications.
2. Contamination control:
- Implement effective sealing solutions to prevent ingress of contaminants like dust, moisture, and debris.
- Regularly clean the surrounding area to minimize the risk of contaminants entering the bearing.
- Use filtered lubrication systems to ensure clean lubricant delivery.
- In dusty or dirty environments, consider using purge systems or positive pressure seals to keep contaminants out.
3. Proper installation and alignment:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for installation procedures and tolerances.
- Use appropriate tools and techniques to ensure correct bearing seating and alignment.
- Verify shaft and housing tolerances before installation to prevent misalignment issues.
- Employ precision alignment tools like laser systems for critical applications.
4. Regular inspections and monitoring:
- Conduct routine visual inspections to check for signs of wear, leakage, or damage.
- Implement condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and oil analysis.
- Use predictive maintenance technologies to detect potential issues before they lead to failure.
- Keep detailed records of inspections and measurements to track bearing performance over time.
5. Temperature control:
- Ensure proper cooling and ventilation of the bearing housing to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Monitor bearing temperatures regularly and investigate any unusual increases.
- Consider using temperature-resistant lubricants in high-temperature applications.
6. Load management:
- Avoid overloading the bearings by adhering to the manufacturer's load ratings.
- Ensure even load distribution across the bearing through proper shaft and housing design.
- Minimize shock loads and vibrations through appropriate machine design and operation practices.
7. Proper handling and storage:
- Store bearings in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature and humidity.
- Handle bearings carefully during installation and maintenance to prevent damage.
- Use appropriate lifting and mounting tools to avoid applying uneven forces during installation.
8. Training and education:
- Provide comprehensive training to maintenance personnel on proper bearing care and handling.
- Keep staff updated on the latest maintenance techniques and technologies specific to four-point contact bearings.
- Encourage a culture of precision maintenance within the organization.
9. Scheduled replacements:
- Develop a proactive replacement schedule based on bearing life calculations and historical performance data.
- Consider replacing bearings during planned shutdowns to minimize disruption to operations.
10. Environmental protection:
- In harsh environments, use protective coatings or materials to shield bearings from corrosive elements.
- Implement proper sealing solutions to protect against moisture ingress in humid or wet environments.
By implementing these strategies, maintenance teams can significantly extend the lifespan of four-point contact ball bearings, reducing downtime and maintenance costs while improving overall equipment reliability. It's important to tailor these practices to the specific application and operating conditions of each bearing to achieve optimal results.
In conclusion, maintaining four-point contact ball bearings requires a comprehensive approach that combines proper installation, regular monitoring, effective lubrication, and contamination control. By understanding the unique characteristics of these bearings and implementing targeted maintenance strategies, organizations can maximize the performance and longevity of their equipment across various industrial applications. Regular training, staying updated with the latest maintenance technologies, and fostering a culture of preventive care are key to ensuring the long-term reliability of systems relying on four-point contact ball bearings.

Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References:
1. SKF Group. (2021). "Four-point contact ball bearings." SKF.com.
2. Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG. (2022). "Four-point contact bearings." Schaeffler.com.
3. NSK Ltd. (2020). "Four-Point Contact Ball Bearings." NSK.com.
4. Timken Company. (2023). "Four-Point Contact Ball Bearings Catalog." Timken.com.
5. American Bearing Manufacturers Association. (2021). "Bearing Maintenance Practices." ABMA.com.
6. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science. (2019). "Advances in Ball Bearing Technology for Industrial Applications."
7. Machinery Lubrication. (2022). "Best Practices for Bearing Lubrication." MachineryLubrication.com.
8. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering. (2020). "Comparative Study of Ball Bearing Types in High-Speed Applications."
9. Plant Engineering. (2023). "Predictive Maintenance Strategies for Industrial Bearings." PlantEngineering.com.
10. Reliability Web. (2021). "Extending Bearing Life Through Proper Maintenance Techniques." ReliabilityWeb.com.

