What are the Applications of Cylindrical Roller?
Cylindrical rollers are crucial components in various mechanical systems, playing a vital role in reducing friction and supporting heavy loads. These precision-engineered elements are widely used across numerous industries due to their unique design and capabilities. Cylindrical rollers are characterized by their cylindrical shape, which allows for excellent load distribution and smooth rotation. Their applications range from automotive and aerospace to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the diverse applications of cylindrical rollers and answer some common questions about their use and benefits.
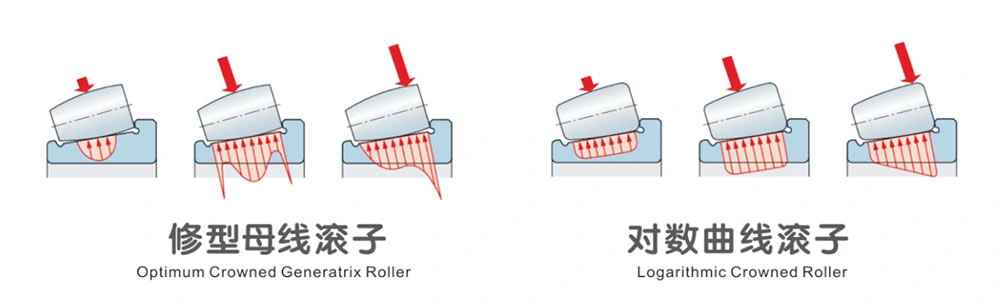
What are the main advantages of using cylindrical roller bearings?
Cylindrical roller bearings offer several significant advantages that make them indispensable in many engineering applications. These benefits stem from their unique design and the properties of the materials used in their construction.
One of the primary advantages of cylindrical roller bearings is their exceptional load-carrying capacity, particularly for radial loads. The cylindrical shape of the rollers provides a larger contact area with the races compared to ball bearings, allowing for better distribution of forces. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications involving heavy loads or where high stiffness is required.
Another key advantage is their ability to accommodate misalignment and shaft deflection to a certain degree. While not as forgiving as spherical roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings can handle small amounts of misalignment without significant performance degradation. This feature is particularly useful in applications where perfect alignment is challenging to maintain, such as in large industrial machinery or long shafts.
Cylindrical roller bearings also excel in high-speed applications. Their design allows for efficient lubrication and heat dissipation, enabling them to operate at higher rotational speeds compared to some other bearing types. This makes them suitable for use in high-speed machinery, such as electric motors, turbines, and machine tool spindles.
Furthermore, these bearings offer low friction performance, which contributes to energy efficiency and reduced wear. The rolling motion of the cylinders generates less friction compared to sliding surfaces, resulting in smoother operation and lower power consumption. This characteristic is especially valuable in applications where energy efficiency is a priority, such as in automotive transmissions or industrial conveyor systems.
Cylindrical roller bearings are also known for their durability and long service life when properly maintained. Their robust construction and the use of high-quality materials allow them to withstand harsh operating conditions, including shock loads and vibrations. This longevity translates to reduced maintenance requirements and lower lifecycle costs for the equipment in which they are installed.
How do cylindrical rollers contribute to industrial machinery performance?

Cylindrical rollers play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of industrial machinery across various sectors. Their unique design and properties contribute significantly to the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of equipment used in manufacturing, processing, and heavy industries.
One of the primary ways cylindrical rollers contribute to industrial machinery performance is through their superior load-carrying capacity. In heavy industrial equipment such as rolling mills, paper machines, and large gearboxes, cylindrical roller bearings can support substantial radial loads while maintaining precise shaft positioning. This capability ensures that machinery operates smoothly and efficiently, even under demanding conditions.
The high stiffness of cylindrical roller bearings is another factor that significantly impacts industrial machinery performance. In precision equipment like machine tools, this stiffness is essential for maintaining accuracy and tight tolerances during operation. By minimizing deflection under load, cylindrical rollers help ensure that cutting tools, grinding wheels, or other machining components maintain their intended positions, resulting in higher quality finished products and reduced scrap rates.
Cylindrical rollers also contribute to improved energy efficiency in industrial machinery. Their low friction characteristics reduce power losses due to bearing friction, which can be substantial in large-scale industrial equipment. This reduction in friction not only leads to lower energy consumption but also reduces heat generation, which can be critical in maintaining the overall thermal stability of the machinery.
In high-speed applications, such as industrial pumps, compressors, and turbines, cylindrical roller bearings excel due to their ability to handle high rotational speeds. Their design allows for effective lubrication and heat dissipation, enabling machinery to operate at peak efficiency without the risk of bearing failure due to excessive heat or inadequate lubrication.
The durability of cylindrical roller bearings is another crucial factor in industrial machinery performance. In environments where equipment is subjected to continuous operation, shock loads, or vibrations, the robustness of these bearings helps maintain consistent performance over extended periods. This durability translates to reduced downtime for maintenance or repairs, improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and productivity.
Cylindrical rollers also contribute to the compact design of industrial machinery. Their high load-carrying capacity relative to their size allows for more compact bearing arrangements, which can lead to smaller and lighter machinery designs. This is particularly beneficial in applications where space is at a premium or where reducing the overall weight of equipment is desirable.
What factors should be considered when selecting cylindrical rollers for specific applications?
Selecting the appropriate cylindrical rollers for specific applications is a critical process that requires careful consideration of various factors. The right choice can significantly impact the performance, reliability, and longevity of the machinery or equipment in which the rollers are installed. Here are the key factors that should be taken into account when making this important decision:
Load Characteristics: One of the primary considerations is the nature and magnitude of the loads that the cylindrical rollers will be subjected to. This includes both radial and axial loads. While cylindrical rollers excel at handling radial loads, certain designs can also accommodate limited axial loads. It's essential to accurately calculate the static and dynamic load ratings required for the application and select rollers that meet or exceed these requirements. Additionally, consider any shock loads or vibrations that may occur during operation, as these can significantly impact the bearing's performance and lifespan.
Speed Requirements: The rotational speed at which the cylindrical rollers will operate is another crucial factor. Different designs and materials are suitable for various speed ranges. For high-speed applications, considerations such as heat generation, lubrication requirements, and cage design become particularly important. Conversely, for low-speed, high-load applications, factors like surface finish and material hardness may take precedence.
Operating Environment: The conditions in which the cylindrical rollers will function play a significant role in their selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, presence of contaminants, and exposure to corrosive substances must be considered. For high-temperature applications, special materials or heat treatments may be necessary. In environments with heavy contamination, enhanced sealing solutions or special lubricants might be required to ensure reliable operation.
Dimensional Constraints: The available space for the bearing installation is often a limiting factor in roller selection. Consider both the radial and axial space limitations of the application. In some cases, a trade-off may be necessary between load capacity and size. The use of standardized sizes can also be beneficial for ease of replacement and maintenance.
Precision Requirements: The level of accuracy and stiffness required in the application will influence the choice of cylindrical rollers. For high-precision machinery, such as machine tools or measuring equipment, rollers with tighter tolerances and higher stiffness may be necessary. The required running accuracy, including considerations of runout and vibration levels, should be factored into the selection process.
Life Expectancy and Reliability: The expected service life of the cylindrical rollers is a critical factor, especially in applications where frequent maintenance or replacement is difficult or costly. Calculate the L10 life (the number of revolutions that 90% of a group of identical bearings will complete or exceed before the first evidence of fatigue develops) based on the application's requirements. Consider the consequences of potential failure and select rollers with appropriate safety factors.
Lubrication Requirements: The type and method of lubrication available or preferred for the application will influence roller selection. Some applications may require oil lubrication for better heat dissipation, while others might be better suited to grease lubrication for simplified maintenance. The accessibility for relubrication and the potential for contamination should also be considered.
Misalignment Tolerance: While cylindrical rollers are not typically designed to accommodate large misalignments, some degree of misalignment may be unavoidable in certain applications. Consider the potential for shaft or housing deflections and select rollers or bearing arrangements that can tolerate the expected level of misalignment without significant performance degradation.
Cost Considerations: While performance should be the primary driver, cost is inevitably a factor in roller selection. Consider not just the initial purchase cost, but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, potential downtime, and replacement. Sometimes, investing in higher quality or more specialized rollers can lead to lower total cost of ownership over the life of the equipment.
Standardization and Availability: Using standardized cylindrical roller designs can offer advantages in terms of availability, interchangeability, and simplified inventory management. However, for specialized applications, custom designs may be necessary to meet specific performance requirements.
Mounting and Dismounting Requirements: Consider how the cylindrical rollers will be installed and removed. Some applications may require frequent dismounting for maintenance, while others may be installed for the life of the equipment. The ease of mounting and dismounting can impact maintenance time and costs.
Noise and Vibration: In applications where low noise and vibration levels are critical, such as in electric motors or precision equipment, special attention should be paid to the selection of cylindrical rollers with appropriate surface finishes, tolerances, and cage designs to minimize these factors.
By carefully considering these factors and consulting with bearing manufacturers or experienced engineers, it's possible to select the optimal cylindrical rollers for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References
1. SKF Group. (2021). Cylindrical roller bearings.
2. Timken Company. (2022). Cylindrical Roller Bearings.
3. NSK Ltd. (2021). Cylindrical Roller Bearings.
4. Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG. (2022). Cylindrical roller bearings.
5. NTN Corporation. (2021). Cylindrical Roller Bearings.
6. American Bearing Manufacturers Association. (2022). Roller Bearings.
7. Koyo Bearings. (2021). Cylindrical Roller Bearings.
8. Machine Design. (2019). What's the Difference Between Roller and Ball Bearings?
9. Engineering360. (2022). Roller Bearings Information.
10. Bearing Tips. (2021). When to use cylindrical roller bearings.

