What Materials Are Commonly Used in Thrust Roller Bearing?
Thrust roller bearings are essential components in various industrial applications, designed to handle significant axial loads while ensuring smooth rotational movement. These specialized bearings are crucial in machinery where forces act parallel to the shaft, such as in gearboxes, thrust blocks, and heavy equipment. The materials used in thrust roller bearings play a vital role in determining their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. This blog post will explore the common materials used in thrust roller bearings, their properties, and how they contribute to the bearing's overall functionality. Understanding these materials is crucial for engineers, manufacturers, and end-users to make informed decisions when selecting or maintaining thrust roller bearings for their specific needs. We'll delve into the characteristics of various materials, their advantages, and the applications where they excel, providing a comprehensive overview of the material science behind these critical mechanical components.
What are the primary materials used in thrust roller bearing components?
Bearing Rings
Thrust roller bearing rings are typically made from high-quality bearing steels, such as AISI 52100 (also known as GCr15 or 100Cr6). This material is chosen for its excellent hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability. The rings are heat-treated to achieve the desired hardness and microstructure, ensuring they can withstand the high stresses and loads experienced during operation. In some cases, stainless steel grades like AISI 440C may be used for corrosion-resistant applications. For thrust roller bearings used in extremely high-temperature environments, heat-resistant steels such as M50 or M50NiL might be employed. These materials allow thrust roller bearings to maintain their performance and structural integrity under demanding conditions.
Rolling Elements
The rolling elements in thrust roller bearings, which can be cylindrical, tapered, or spherical rollers, are typically made from the same high-quality bearing steels as the rings. AISI 52100 is the most common choice due to its excellent hardness and wear resistance. These rollers are precision-ground to tight tolerances and may undergo additional surface treatments to enhance their performance. For applications requiring higher corrosion resistance, stainless steel rollers may be used. In some specialized thrust roller bearings designed for extreme conditions, ceramic materials like silicon nitride (Si3N4) might be employed for the rolling elements. Ceramic rollers offer advantages such as lower density, higher hardness, and better electrical insulation properties compared to steel, making them suitable for high-speed or electrically sensitive applications.
Cage Materials
The cage in a thrust roller bearing plays a crucial role in maintaining proper spacing between the rolling elements and guiding them during operation. Various materials are used for cages, depending on the application requirements. For standard thrust roller bearings, brass is a common cage material due to its good machinability, wear resistance, and ability to withstand moderate temperatures. Steel cages, either pressed steel or machined steel, are used in applications requiring higher strength and durability. For high-speed or high-temperature applications, polymer cages made from materials like polyamide (nylon) or PEEK (polyether ether ketone) may be employed. These materials offer low friction, good wear resistance, and the ability to operate in challenging environments. In some cases, phenolic resin cages reinforced with cotton fabric are used for their excellent oil retention properties and ability to withstand high temperatures.
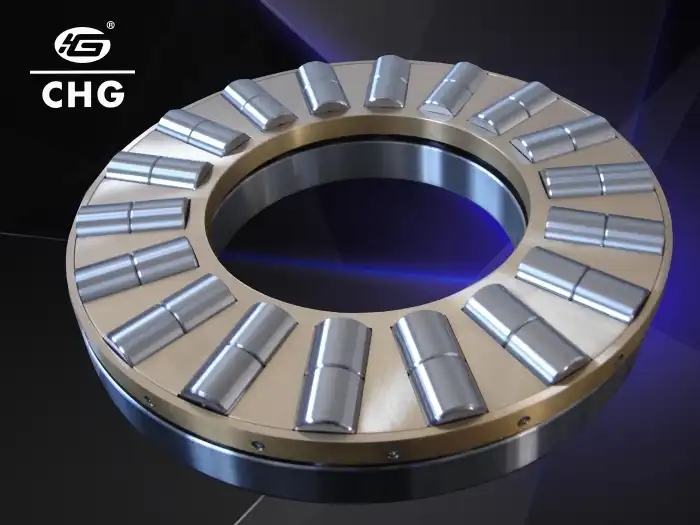
How do material choices affect thrust roller bearing performance?
Load Capacity and Durability
The choice of materials significantly impacts the load capacity and durability of thrust roller bearings. High-quality bearing steels like AISI 52100 used in rings and rolling elements provide excellent hardness and wear resistance, allowing thrust roller bearings to handle heavy axial loads and maintain their performance over extended periods. The hot treatments that are used on these materials make them even stronger and last longer. For example, through-hardened bearings have a hardness that stays the same throughout the part, while case-hardened bearings have a harder top layer and a softer core, which makes them better at resisting wear and pressure. The type of material used for the cage also affects how long it lasts. Metal cages are very strong, while polymer cages are resistant to wear and have low friction.
Operating Temperature Range
Material selection is crucial in determining the operating temperature range of thrust roller bearings. Standard bearing steels like AISI 52100 perform well up to temperatures around 120°C (248°F). For higher temperature applications, special heat-resistant steels or tool steels may be used, allowing operation at temperatures up to 300°C (572°F) or even higher. The temperature performance is also affected by the type of cage material. Brass and steel cages work well in low temperatures, while high-performance plastics like PEEK can handle higher temperatures. In the worst situations, ceramic rolling parts may be used to make the temperature range even wider. It is very important for many industrial uses that thrust roller bearings can keep their shape and mechanical qualities over a wide temperature range. This is especially true in machining, chemical processing, and power generation.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a key factor in choosing the right material for thrust roller bearings, especially when they will be used in tough settings or with corrosive media. Standard bearing steels work well in most situations, but they may rust in harsh circumstances. For rings and rolling parts, types of stainless steel like AISI 440C can be used to make them more resistant to rust. These materials have a good mix of strength, resistance to wear, and defense against corrosion. In extreme cases, ceramic materials like silicon nitride can offer superior corrosion resistance. The choice of cage material also impacts corrosion resistance, with brass and polymer cages generally offering better resistance compared to steel cages. Some thrust roller bearings may also incorporate special coatings or surface treatments to enhance their corrosion resistance, further expanding their application range in corrosive environments.

What are the latest material innovations in thrust roller bearing design?
Advanced Steel Alloys
Recent advancements in metallurgy have led to the development of new steel alloys specifically designed for thrust roller bearings. Compared to regular bearing steels, these new materials are better at combining strength, stiffness, and wear resistance. For instance, carburizing steels with carefully managed metal mixtures can make the surface harder while keeping the core tough. This makes bearings that last longer and can hold more weight. Some of these new metals are also better at keeping their shape at high temperatures, which means that thrust roller bearings can be used in a wider range of temperatures. To meet the growing needs of modern industrial uses, manufacturers are always studying and creating new steel compositions. What this does is push the edges of what thrust roller bearings can do.
Ceramic and Hybrid Bearings
The use of ceramic materials in thrust roller bearings has been gaining traction in recent years. Full ceramic bearings, where both rings and rolling elements are made from materials like silicon nitride, offer exceptional performance in terms of wear resistance, high-speed capability, and electrical insulation. However, their higher cost and brittleness can limit their application. A more usual method is to use hybrid bearings, which have both steel rings and ceramic rolling parts. These hybrid thrust roller bearings are a good mix of performance and cost-effectiveness. Better things about them are that they have less friction, go faster, and keep oil from breaking down better. Since ceramic rolling elements are light, they also lower the forces that cause them to spin at high speeds. Because of this, they work great in high-speed pumps, machine tools, and airplanes.
Polymer Composites
Innovative polymer composites are finding their way into thrust roller bearing designs, particularly for cage materials. These high-tech materials mix the good qualities of polymers, like low friction and good wear resistance, with reinforcing threads or particles to make them stronger and better able to handle high temperatures. For example, carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK cages offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high temperature resistance, and self-lubricating properties. Polymer blend coats are also being tried on bearing parts by some companies to make them better at rubbing against each other and stopping rust. These materials give thrust roller bearings new uses in places where standard materials might not work well, like where chemicals are present or where little grease is needed. As research in polymer science continues, we can expect to see even more advanced materials making their way into thrust roller bearing designs, further improving their performance and expanding their application range.

Conclusion
The materials used in thrust roller bearings play a crucial role in their performance, durability, and application suitability. From high-quality bearing steels to advanced ceramics and polymer composites, each material choice offers unique properties that cater to specific operational requirements. As technology advances, we can expect further innovations in material science to enhance thrust roller bearing capabilities, meeting the ever-increasing demands of various industries. For those seeking high-quality thrust roller bearings and expert guidance, Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. offers a wide range of solutions. With their extensive experience and commitment to innovation, they can provide tailored bearing solutions to meet your specific needs. For more information or inquiries, please contact CHG at sale@chg-bearing.com.
FAQ
What is the most common material used for thrust roller bearing rings?
The most common material for thrust roller bearing rings is AISI 52100 (GCr15 or 100Cr6) bearing steel, known for its excellent hardness and wear resistance.
Can ceramic materials be used in thrust roller bearings?
Yes, ceramic materials like silicon nitride can be used for rolling elements in thrust roller bearings, offering benefits such as lower density, higher hardness, and better electrical insulation.
What are the advantages of using polymer cages in thrust roller bearings?
Polymer cages offer low friction, good wear resistance, and the ability to operate in challenging environments, making them suitable for high-speed or high-temperature applications.
How do material choices affect the corrosion resistance of thrust roller bearings?
Material choices significantly impact corrosion resistance. Stainless steel grades and ceramic materials offer improved corrosion protection compared to standard bearing steels.
What are hybrid bearings in the context of thrust roller bearings?
Hybrid bearings combine steel rings with ceramic rolling elements, offering a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness with benefits like reduced friction and higher speed capabilities.
References
1. Smith, J. D. (2013). "Modern Tribology Handbook, Two Volume Set." CRC Press.
2. Harris, T. A., & Kotzalas, M. N. (2006). "Essential Concepts of Bearing Technology." CRC Press.
3. Eschmann, P., Hasbargen, L., & Weigand, K. (1985). "Ball and Roller Bearings: Theory, Design and Application." John Wiley & Sons.
4. Harnoy, A. (2002). "Bearing Design in Machinery: Engineering Tribology and Lubrication." CRC Press.
5. Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG. (2019). "Rolling Bearing Catalogue."
6. SKF Group. (2018). "Rolling Bearings Catalogue."

