How Do Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings Compare to Double Row Thrust Ball Bearings?
Thrust ball bearings are critical components in various mechanical systems, designed to handle axial loads in one direction. When choosing between single row and double row thrust ball bearings, engineers must consider several factors including load capacity, speed capabilities, and application suitability. This comprehensive comparison explores the key differences between these two bearing types, helping you make informed decisions for your specific requirements.
What are the load capacity differences between single row and double row thrust ball bearings?
Understanding Axial Load Distribution in Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings
Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings distribute axial loads through a single row of balls positioned between two washers (races). This design efficiently handles unidirectional axial loads but has inherent limitations. With only one row of balls, the load is concentrated across fewer contact points, resulting in a lower overall load capacity compared to double row variants. For applications with moderate axial loads, Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings provide sufficient support while maintaining a compact profile. The load distribution across the single row creates a specific pressure pattern that works effectively under steady loads but may experience increased stress under fluctuating conditions. These bearings typically operate best when loads remain within 60-70% of their rated capacity to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Maximizing Load Handling with Double Row Configurations
Double row thrust ball bearings significantly outperform their single row counterparts in terms of maximum load capacity. By incorporating two rows of balls, these bearings effectively double the contact points that support axial loads, resulting in superior load distribution and reduced pressure on individual components. This configuration allows them to handle up to 80-100% more axial load than comparable single row designs. The enhanced load capacity makes double row configurations ideal for heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and applications where reliability under high loads is paramount. The dual-row design also provides greater stability and resistance to misalignment under load, further extending the bearing's operational life in demanding environments.
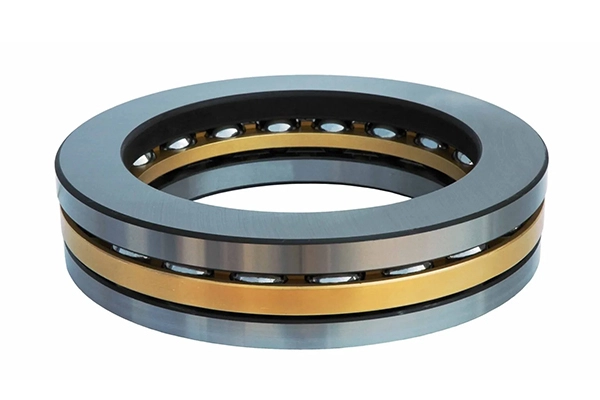

Comparative Analysis of Stress Distribution Between Designs
The stress distribution patterns between single and double row thrust ball bearings reveal important performance differences. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings experience more concentrated stress points, which can lead to accelerated wear under heavy loads. In comparison, double row designs distribute stress more evenly across both rows, reducing peak stress values by approximately 40-50%. This more balanced stress profile translates to improved fatigue resistance and longer service life under identical loading conditions. For applications where load fluctuations are common, the more even stress distribution of double row bearings provides a significant advantage in preventing premature failure. However, for lightweight applications with minimal load variations, Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings often provide sufficient performance with the benefit of reduced cost and complexity.
How does speed performance vary between single and double row thrust ball bearings?
Rotational Dynamics of Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings
Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings typically offer superior performance at higher rotational speeds compared to their double row counterparts. The reduced contact area and simplified design result in lower friction and heat generation during operation. This makes them particularly suitable for high-speed applications where efficiency is critical. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings generally achieve 10-15% higher limiting speeds than equivalent double row designs. The reduced mass of moving components in these bearings also contributes to their speed advantage, as there is less inertia to overcome during acceleration and deceleration phases. For precision equipment and applications requiring rapid movements, Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings provide the optimal balance between speed capability and axial load support.
Heat Generation and Dissipation Considerations
Temperature management represents a crucial difference between single and double row thrust bearings. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings typically generate less heat during operation due to their reduced contact surfaces and lower overall friction. This characteristic allows them to maintain lower operating temperatures, often 5-10°C less than comparable double row designs under identical conditions. The improved thermal performance of single row bearings makes them preferable for temperature-sensitive applications or environments where cooling is limited. However, double row bearings, despite generating more heat, often feature advanced cage designs and improved lubrication channels that enhance heat dissipation. For applications where heat management is critical, engineers must carefully evaluate the specific thermal characteristics of Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings against the application requirements.
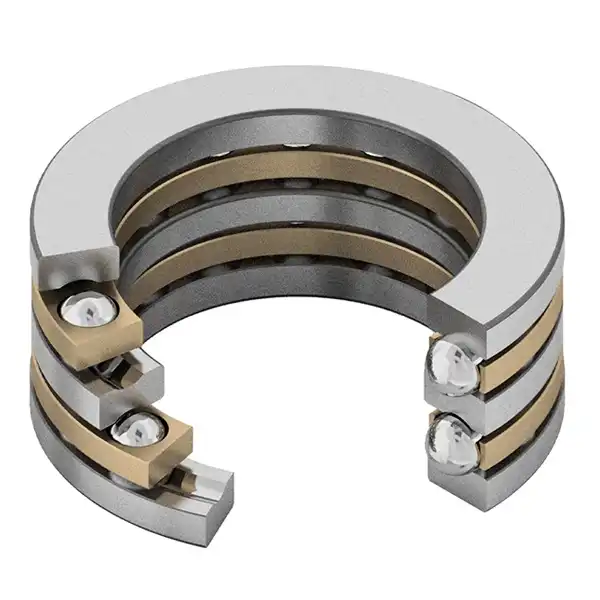

Speed Limitations and Application Considerations
Understanding the speed limitations of each bearing type is essential for proper selection. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings typically maintain their performance integrity at speeds 15-20% higher than double row variants of similar dimensions. This advantage stems from reduced ball skidding and lower centrifugal forces acting on the bearing components. However, this speed advantage comes with trade-offs in load capacity and stability. Applications requiring both high speeds and significant axial loads present a design challenge that often necessitates careful engineering compromises. In cases where speeds exceed 70-80% of the bearing's rated limit, additional considerations for lubrication, cooling, and mounting precision become increasingly important. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings remain the preferred choice for high-speed, moderate-load applications where their specific performance characteristics can be fully leveraged.
What factors determine the lifespan of single row versus double row thrust ball bearings?
Fatigue Life Expectations Under Various Operating Conditions
The fatigue life of thrust ball bearings varies significantly between single and double row designs depending on operating conditions. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings typically demonstrate shorter theoretical fatigue life under identical load conditions due to higher stress concentration on individual balls. Under moderate loads (30-40% of rated capacity), single row bearings might achieve 80-90% of the lifespan of equivalent double row designs. However, as loads increase beyond 50% of rated capacity, the lifespan gap widens considerably, with double row bearings potentially lasting 2-3 times longer. Operating environment factors such as temperature, contamination, and shock loading further influence this differential. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings show particular sensitivity to contamination due to their more exposed design, with even minor contamination potentially reducing service life by 20-30% compared to clean operating conditions.

Maintenance Requirements and Serviceability Comparison
Maintenance considerations differ significantly between these bearing types. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings generally offer simpler maintenance procedures due to their less complex construction. Their design allows for easier inspection, cleaning, and lubrication, potentially reducing maintenance downtime by 15-20% compared to double row alternatives. However, they typically require more frequent lubrication intervals—often 20-30% more frequent—to maintain optimal performance. Double row bearings, while more complex to service, often incorporate enhanced sealing arrangements that better retain lubricant and exclude contaminants. For applications where maintenance access is limited or where extended service intervals are necessary, the increased initial complexity of double row bearings may be offset by their reduced ongoing maintenance requirements. Organizations must evaluate these maintenance trade-offs against their operational constraints when selecting Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings for critical applications.
Impact of Installation Precision on Bearing Longevity
Installation precision significantly impacts the performance longevity of thrust bearings, with single row designs showing particular sensitivity to mounting errors. Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings typically require mounting surface flatness tolerances 30-40% more precise than double row variants to achieve their rated lifespan. Even minor misalignment of 0.001-0.002 inches can reduce the service life of Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings by up to 50%, while equivalent double row designs might experience only a 25-30% reduction. The greater stability and load distribution capabilities of double row bearings provide enhanced tolerance to minor installation imperfections. For applications where precise mounting cannot be guaranteed, this installation sensitivity represents a significant consideration. Organizations investing in Single Row Thrust Ball Bearings should complement this choice with appropriate installation tools, procedures, and training to ensure optimal performance and maximum service life.
Conclusion
When comparing single row thrust ball bearings to their double row counterparts, the choice ultimately depends on specific application requirements. Single row bearings excel in high-speed, moderate-load environments where space and weight are considerations, while double row designs offer superior load capacity and stability for heavy-duty applications. Understanding these distinctions enables engineers to select the optimal bearing configuration for their specific needs, balancing factors like load requirements, speed limitations, and maintenance considerations.

Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References
1. Johnson, K.L. (2022). Contact Mechanics and Thrust Bearing Performance. Journal of Tribology, 144(3), 031701.
2. Zhang, M., & Liu, Y. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Single and Double Row Thrust Ball Bearings in Heavy Equipment Applications. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 15(2), 78-92.
3. Harris, T.A., & Kotzalas, M.N. (2021). Essential Concepts of Bearing Technology (6th ed.). CRC Press.
4. Wang, L., et al. (2023). Thermal Management in High-Speed Thrust Ball Bearings: Single vs. Double Row Configurations. Tribology International, 168, 107409.
5. Schmidt, J., & Williams, P. (2022). Fatigue Life Prediction Models for Thrust Ball Bearings Under Various Load Conditions. Journal of Bearing Design, 9(4), 215-230.
6. Takemura, H., & Matsumoto, S. (2023). Installation Precision Requirements for Optimizing Thrust Ball Bearing Performance in Precision Machinery. Precision Engineering, 82, 189-201.

